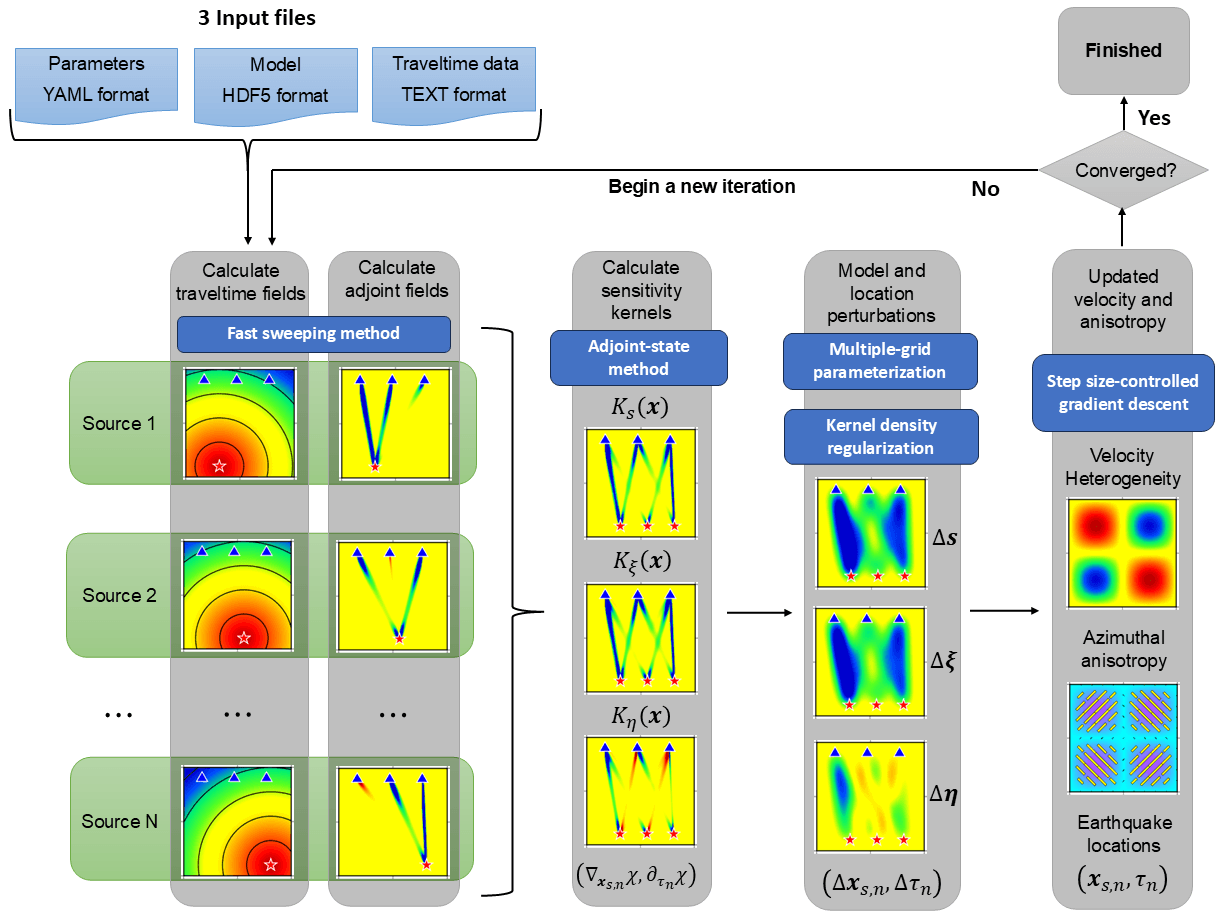
TomoATT is a numerical library for adjoint-state travel-time tomography, which is developed for :
- computing with a very large and fine forward grid,
- large number of earthquake sources and stations dataset in
- an efficient and scalable way on modern HPCs.
Thanks to the efficiency of an eikonal equation solver, the computation of the travel-time is very fast and requires less amount of computational resources. As an input data for TomoATT is travel times at seismic stations, we can easily process a great amount of input data for the computation.
Currently TomoATT family is supporting:
- velocity and azimuthal anisotropy inversion for regional and teleseismic events (TomoATT)
- velocity inversion surface wave dispersion data (SurfATT)
- velocity inversion for reflection (e.g., PmP) and refraction data (e.g., Pn) (RefATT)
- Body wave attenuation tomography is under development.
Citation
The TomoATT implements the methods described in the publications:
-
The TomoATT software package
- Chen, J., Nagaso, M., Xu, M., & Tong, P. (2025). TomoATT: An open-source package for Eikonal equation-based adjoint-state traveltime tomography for seismic velocity and azimuthal anisotropy. Computers & Geosciences, 105995. DOI .
-
Regional tomography in Cartesian coordinates
-
Tong, P. (2021). Adjoint‐state traveltime tomography: Eikonal equation‐based methods and application to the Anza area in southern California. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 126(5), e2021JB021818. DOI .
-
Tong, P. (2021). Adjoint‐state traveltime tomography for azimuthally anisotropic media and insight into the crustal structure of central California near Parkfield. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 126(10), e2021JB022365. DOI .
-
-
Regional tomography in Spherical coordinates
- Chen, J., Chen, G., Nagaso, M., & Tong, P. (2023). Adjoint-state traveltime tomography for azimuthally anisotropic media in spherical coordinates. Geophysical Journal International, 234(1), 712-736. DOI .
-
Teleseismic tomography in Spherical coordinates
- Chen, J., Wu, S., Xu, M., Nagaso, M., Yao, J., Wang, K., … & Tong, P. (2023). Adjoint‐state teleseismic traveltime tomography: Method and application to Thailand in Indochina Peninsula. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 128(12), e2023JB027348. DOI .
High Accuracy
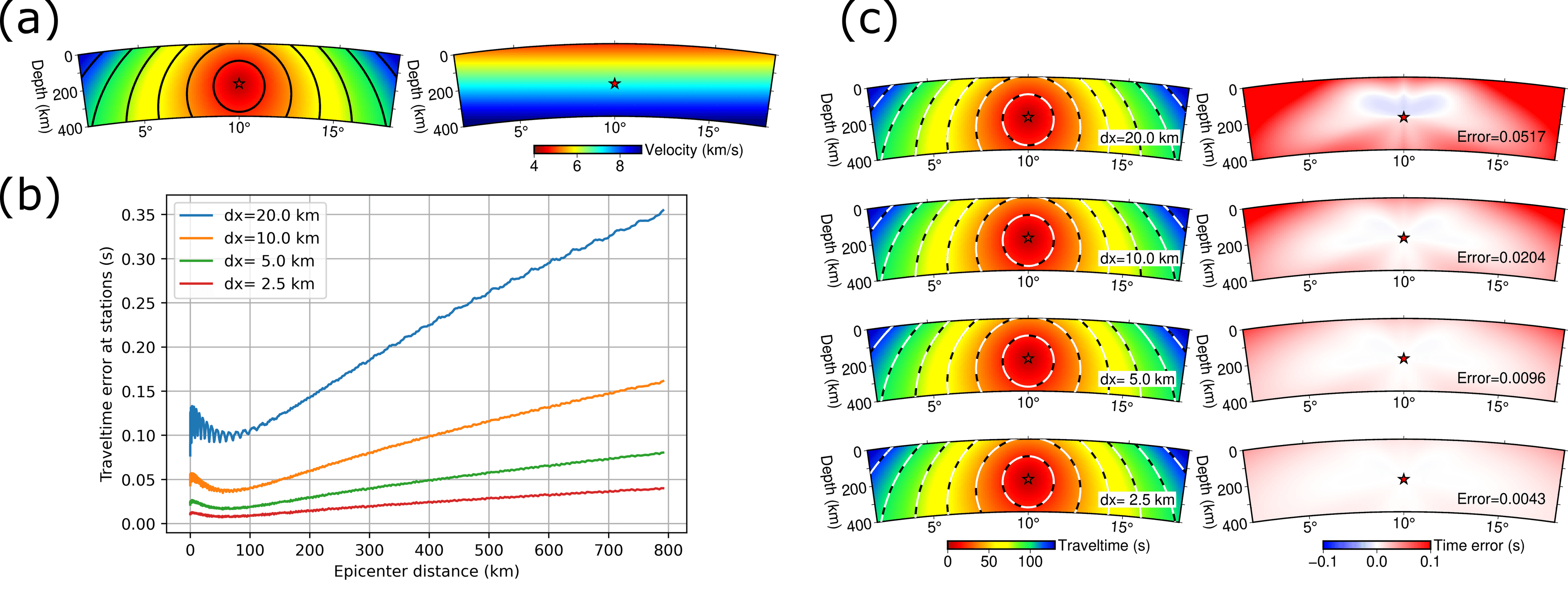
TomoATT solves the anisotropic Eikonal equation for the traveltime field of wavefront propagation from the source to any positions within the study region. We select the fast sweeping method (FSM) as the Eikonal solver. This grid-based method has proven unconditionally convergent to the solution, and achieves the optimal computational complexity of, where is the total number of grid nodes. Additionally, we use the multiplicative factorization technique to eliminate source singularity and solve the equation in spherical coordinates to account for Earth’s curvature, further improving accuracy. This image show a toy model to evaluate the accuracy of FSM for calculating traveltime.
High Performance
For modeling a very large and fine grid with numerous seismic events, this library applies 3-layer parallelization, which are:
- layer 1: simultaneous run parallelization (travel times for multiple seismic sources may be calculated simultaneously)
- layer 2: subdomain decomposition (If the number of computational nodes requires too large memory, we can separate the domain into subdomains and run each subdomain in a separate compute node)
- layer 3: sweeping parallelization (in each subdomain, sweeping layers are also parallelized)

Related publications
-
Hao, Shijie, Jing Chen, Mijian Xu, and Ping Tong. “Topography‐Incorporated Adjoint‐State Surface Wave Traveltime Tomography: Method and a Case Study in Hawaii.” Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth 129, no. 1 (2024): e2023JB027454.
-
Tong, Ping, Tianjue Li, Jing Chen, and Masaru Nagaso. “Adjoint-state differential arrival time tomography.” Geophysical Journal International 236, no. 1 (2024): 139-160.
-
Chen, Jing, Shucheng Wu, Mijian Xu, Masaru Nagaso, Jiayuan Yao, Kai Wang, Tianjue Li, Yiming Bai, and Ping Tong. “Adjoint‐State Teleseismic Traveltime Tomography: Method and Application to Thailand in Indochina Peninsula.” Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth 128, no. 12 (2023): e2023JB027348.
-
Chen, Jing, Guoxu Chen, Masaru Nagaso, and Ping Tong. “Adjoint-state traveltime tomography for azimuthally anisotropic media in spherical coordinates.” Geophysical Journal International 234, no. 1 (2023): 712-736.
-
Qi, Yingyu, and Ping Tong. “Structure of the Crustal Magmatic System in the Geysers‐Clear Lake Area (Northern California) Imaged by Adjoint‐State Travel‐Time Tomography.” Seismological Society of America 94, no. 1 (2023): 414-427.
-
Wang, Kai, Shucheng Wu, and Ping Tong. “Crustal Deformation in the Sierra Nevada and Walker Lane Region Inferred From P‐Wave Azimuthal Anisotropy.” Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth 127, no. 12 (2022): e2022JB024554.
-
Wu, Shucheng, Chengxin Jiang, Vera Schulte‐Pelkum, and Ping Tong. “Complex patterns of past and ongoing crustal deformations in Southern California revealed by seismic azimuthal anisotropy.” Geophysical Research Letters 49, no. 15 (2022): e2022GL100233.
-
Tong, Ping. “Adjoint‐state traveltime tomography for azimuthally anisotropic media and insight into the crustal structure of central California near Parkfield.” Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth 126, no. 10 (2021): e2021JB022365.
-
Tong, Ping. “Adjoint‐state traveltime tomography: Eikonal equation‐based methods and application to the Anza area in southern California.” Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth 126, no. 5 (2021): e2021JB021818.
